Diet & Nutrition General Guidelines:
Both men and women’s metabolisms are very similar, but women burn a greater ratio of fat to carbs. The only thing that will need adjusting is the total caloric intake. Women need fewer calories than men, this is due to men having more muscle mass and less fat than women. The amount of protein, carbs and fat will be balanced by the amount of calories eaten. If you are trying to gain lean muscle, you will need to eat adequate protein and essential fatty acids.
The biggest factor in a diet is calories. Too many calories will lead to weight gain. Too lesser calories will not gain lean muscle. Setting a target calorie intake is vital to losing fat and gaining muscle.
Female Hormones And Lifting:
Testosterone is responsible for the increases in muscle mass. Women’s testosterone levels are significantly lower than men’s testosterone levels. Testosterone levels in men are between 200-1200 ng/dl, women are between 15-70 ng/dl. With this information we can show that lifting heavy weights will not make you bulky or manly as women do not have the hormonal support to gain muscle mass like men.
If you want to gain muscle and improve your shape and curves, then you need to lift heavy. Instead of doing continuous reps with light weights, you need to add some weight. Performing high rep sets (15-20 reps) does have benefits, but it does not target muscle mass.

Related article: How Many Calories Do I Need To Eat Per Day To Build Muscle?
Macro-nutrient Manipulation:
While your total caloric intake is important, the ratio of protein to carbs to fat will determine whether the weight you gain or lose is muscle or fat. A diet containing 80% of calories from carbs, 10% from protein and 10% from fat, will differ the results from a diet containing 40% of calories from carbs, 40% from protein and 20% from fat.
Keep Hydrated:
Try to drink at least eight glasses of water a day. Benefits from drinking water are optimal hydration as well as feeling full without added food intake. Sometimes thirst can be mistaken for hunger, so staying hydrated can prevent overeating.
Quality Control:
Choose fresh, wholesome foods. Packaged foods contain added preservatives, especially sodium and saturated fats plus they often have high amounts of sugars.
Insulin:
Insulin is the storage hormone. When insulin is secreted, fat burning is stopped. You can control insulin secretion by choosing low GI carbs, this can decrease fat gain and increase fat loss. Stable insulin levels also improves energy levels and moods.
Protein:
To gain lean muscle you need to consume enough protein to sustain new muscle proteins. You may not be used to eating a larger amount of protein, but once you get into the habit you will enjoy how full and satisfied you feel.
Essential Fats:
Essential fatty acids (EFAs) are vital to the functioning of your body. EFAs are needed by the body and are part of a healthy diet. Eating fats does not mean you will gain fat. EFAs support the fat burning process and help maintain a lean body.
Exercises That Add Curves
The most common thing you do in the gym is cardio, or lift weights that are 5 pound dumbbells and do continuous reps. Women need to lift heavy, more challenging weights in order to gain muscle. Machines do provide sufficient muscle stimulation but nothing can benefit more than free-weight or compound exercises.
Deadlifts
Deadlifts are a full body exercise, they stimulate just about every muscle in the body. Deadlifts target the:
- Legs.
- Back.
- Traps.
- Abs.
- Obliques.
Deadlifts are essential for achieving a fully developed body.
Squats
Squats are effective exercises for overall leg development and glute shaping. Free weight barbell squats are a compound exercise that targets the:
- Entire upper leg.
- Quadriceps.
- Hamstrings.
- Glutes.
Like the deadlift, if you don’t squat you are missing out on toned legs and shapely glutes.
Lunges
Lunges are great for targeting the:
- Glutes.
- Hamstrings.
- Quadriceps.
Lunges will help tighten and shape your legs and glutes.
Pull-Ups
Pull-ups target the:
- Back.
- Biceps.
- Forearms.
- Abs.
Most gyms have an assisted pull-up machine or bands, so if you struggle to pull your own bodyweight, these are perfect to assist you and help you to shape your upper half.
Dips
Dips target the:
- Chest.
- Shoulders.
- Triceps.
Dips are great for overall upper body development.
The majority of gyms have an assisted dip machine, this machine will assist you to lift your own bodyweight.
Related article: Muscle Building Tips For Women
The 12-Week Workout Programme:
Most women begin working out with a goal are to tone up and gain curves, following this programme will help you achieve this! You are now going to decrease the number of reps you complete and increase the weight lifted as you progress. The number of sets stays the same, but the rep range changes per exercise.
Weeks 1-4:
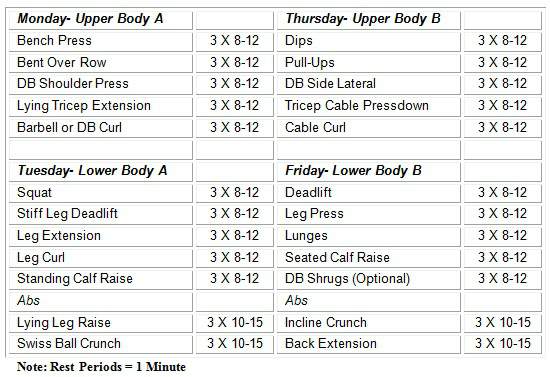
During weeks 1-4, you will lift between 8-12 reps. Aim to complete at least 8 reps but no more than 12 reps for each set. If you cannot complete 8 reps, then reduce the weight. If you find 12 reps easy, increase the weight.
Weeks 5-8:
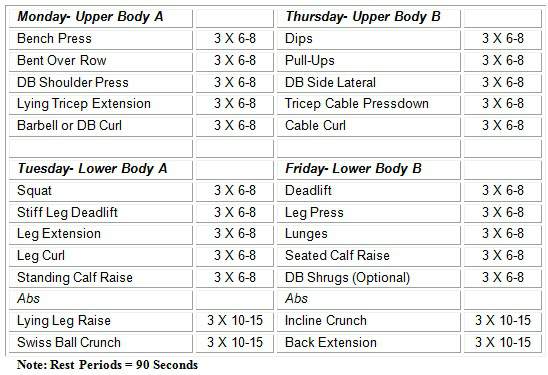
Weeks 5-8, you will lift in the 6-8 rep range. You want to complete at least 6 reps but no more than 8 reps for each set. If you cannot complete 6 reps, decrease your weight. If you complete more than 8 reps, decrease weight.
Weeks 9-12:

During weeks 9-12, you will be lifting 4-6 reps. Complete at least 4 reps but no more than 6 reps for each set. If you cannot complete 4 reps, decrease your weight. If you complete more than 6 reps, increase the weight.
Tips:
It is important to maintain strict form with all movements. This means stabilising your body and contracting your abs so you can hold your posture correctly. By contracting your abs you do not rock or swing the weight, you stabilise your body and prevent momentum. This will also help tone your abs and save your lower back from injury.
Continue Reading on PAGE 2


