I’m sure you’ve noticed the guys that have muscles that are so full and round that they seem to show off the body with perfection, while we have muscles that are visually less voluminous, maybe even flat.
This article is for those of us in the latter group who could use a boost in muscle fullness.
Although we may never be able to match the genetically gifted men of fullness like Mr. Olympia Phil Heath, we can all significantly, even dramatically, increase the fullness of our muscle bodies by using one or more of the following strategies.
1. Increase Time Under Tension
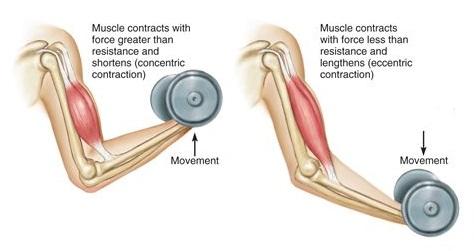
Time under tension (TUT) is about the amount of time the working muscle is under tension, as in contracting, during a given set.
Whether it’s concentric, eccentric, or isometric, muscle contraction increases the tension within a muscle. For purposes of filling out flat muscles, it’s the effects of a longer TUT, specifically the effect of blood vessel occlusion.
When a muscle is contracting, the blood vessels within it are squashed to the point of being occluded, dramatically reducing blood flow to that muscle.
The longer the muscle is contracting, the longer the blood flow is stopped. Your heart is still pumping blood during your set, so this occlusion results in more blood volume building up on the upstream side of the working muscle.
When your set is completed and the muscle relaxes, blood rushes into the muscle.
The longer the blood is occluded, the higher the volume of blood suddenly surging into the muscle. To literally feel this at work, do push-ups for five seconds and note the pump you get after. Now rest a couple minutes and then do push-ups for 30 seconds, again noting the subsequent influx of blood.
Whether you call it hyperaemic super-compensation or a pump, this sudden surge of blood flow and increased blood volume increases the pressure within the muscle. However, what we’re after is the increase in outward pressure, this increase in blood volume places on the tough, dense, fascia that surrounds the muscle.
Fascia isn’t easy to stretch, but over time it does respond to pressure by expanding and subsequently causing an increase in the volume and visual fullness of the muscle it surrounds.
Increasing TUT does, in fact, lead to an increase in muscle fullness. It takes time, no doubt, but it does occur. Using more resistance and a higher rep speed is advantageous in terms of motor unit recruitment (a.k.a. recruiting more muscle fibres).
Instead of prolonging TUT by doing reps more slowly with a lighter weight, it’s better to still move the weight quickly (at least concentrically) and to only lighten the weight as much as is needed to increase the TUT to around 45 seconds or so.
If a set takes less than 30 seconds, it’s not going to be optimal in terms of increasing intramuscular pressure. But, going longer than 60 seconds isn’t generally optimal either, because it requires using a weight that is too light. Performing a TUT of about 45 seconds is the target.
2. More Volume
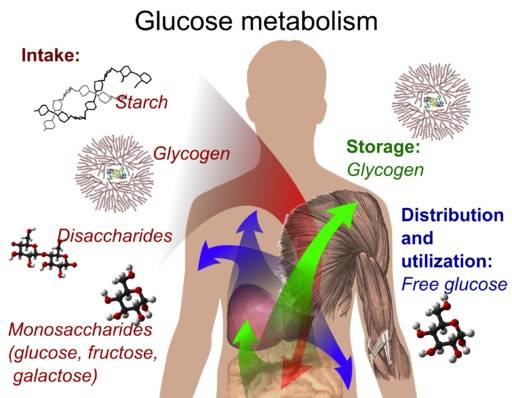
By volume it’s the combination of sets and reps. In essence, it’s the overall amount of work a muscle does during a workout. More work means more energy is needed for that work. This is about muscle glycogen, the stored carbs within a muscle.
Let’s say you’re going to apply the above expansion and do sets of, for example, twelve reps during your chest workout. Doing 10 sets of 12 reps uses far more pectoral glycogen than does doing just two sets of 12. (Glycogen comes from the muscle being worked.)
When we do a training session with enough volume to deplete muscle glycogen within a muscle. The body responds by trying to store more muscle glycogen in that muscle so that you’re better able to handle the same workout the next time around.
The short-term increase in muscle glycogen is called glycogen super-compensation. This results in your muscles temporarily being able to store more glycogen than they could normally hold.
In the long run your body is still working to gradually build the capacity to store more glycogen and it will if you keep taxing glycogen stores. So this increase in muscle glycogen is both a short-term and long-term strategy.
Although we’re not arbitrarily concerned about more intramuscular glycogen storage, we are concerned about muscle fullness. A muscle that stores more glycogen is a rounder, fuller, muscle.
As with any training adaptation, this isn’t something you’ll necessarily see after a high volume workout, but it is something you’ll notice over time.
If you’ve already been using a relatively high volume of training, then you’re not growing experience, if any, adaptation, simply because you’ve already been doing it. The same applies to increasing TUT.
The other reason you may not see and experience the muscle fullness that you should isn’t training related, it’s diet related. If you don’t consume enough carbs, especially in the post-workout window of increased sensitivity to glycogen storage, then your body simply doesn’t have the fuel with which to fill your muscles up with glycogen.
Glycogen is simply stored carbs, not stored protein or fat. You have got to put ample carbs in your body to fully replenish muscle glycogen stores.
It’s worth pointing out that, if you’re chronically storing more glycogen within the muscle, the surrounding fascia is also receiving the pressure to stretch.
But you must keep in mind that volume and intensity simply must be inversely proportional to allow for complete muscular and nervous system recuperation. So, avoid the temptation to take every set of a high volume program to failure.
3. Optimise Rest Periods
Similar to the first strategy, optimising rest periods between sets relates to maximising blood volume and pressure within the muscle.
Imagine doing a set that really has you pumped. Now you decide to rest 3 minutes in order for your body to remove lactic acid, buffer hydrogen ions and replenish creatine phosphate (CP) stores as much as possible. In terms of performance on the upcoming set, this is a great idea.
But in terms of sustaining the increase in intramuscular blood volume, resting 3 minutes is not a good idea. You can probably feel your imaginary pump fading just thinking about resting 3 minutes.
Fascia is a tough, dense type of tissue. It doesn’t just expand because a little pressure is put on it for a few moments. Instead, it takes amounts of sustained pressure to eventually get it to expand.
In order to maximise fascia expansion and muscle fullness, once you’ve got a muscle full of blood, you want to keep it full of blood for as long as possible. Doing so provides more of a stimulus for fascia expansion.
As with every technique, there are pros and cons. If you resume your next set too soon, your performance on the following set will suffer. It does take time to clear waste products and replenish CP stores, both of which are important if you plan to get a decent number of reps on the following set.
If you rest too long, you’re going to release the outward pressure on the fascia.
By paying close attention to the tightness and fullness after a set and especially, when that fullness begins to dissipate, you can finely tune your rest periods to optimise fascia stretch.
If you get 15 reps on set one but only six reps on set two, then you didn’t rest long enough.
If you combine your attentiveness to the dissipation of intramuscular pressure with your performance on subsequent sets, you can finely tune your rest periods for fascia expansion.
Thirty to sixty seconds is a good range to stay within. Generally toward the lower side on less taxing things like biceps curls, and toward the longer end on more taxing movements like squats, that is if you’re ever feeling ready to try squats with just 60 seconds of rest.
4. Stretch Whilst Full
Stretching a muscle while it’s full of blood.
This is one of the most undervalued tools we have available to us, both in terms of performance and injury prevention, as well as appearance.
Stretching itself helps to reduce the constrictive force fascia puts on muscle. And it’s especially effective in terms of fascia expansion if it’s held for a longer period of time. Think longer TUT for stretching, too.
In order to maximise the expansive force placed on the surrounding fascia during a stretch, do the stretch while that muscle is still full of blood. Stretch within 30 seconds of completing a high TUT set. Then, as opposed to your typical ten second stretch, hold the stretch for a while. Try 60 seconds or even more.
Because static stretching appears to decrease power on subsequent sets, plan to do this long-hold stretching after completing the last set for that particular body part.
There’s also another benefit to stretching in regards to muscle fullness other than putting tension on and expanding the fascia. It appears that if done with ample tension and duration, stretching actually stimulates the muscle to lengthen by laying down new sarcomeres.
If, we can get a muscle to add length via new sarcomeres, then that muscle will have more overall volume and will appear fuller, especially when flexed.
But as with any of these techniques that rely on fascia expansion, it takes time and consistency. Make yourself a reminder to stretch after training or you’ll forget.Plan on at least 3 months of implementation before seeing changes. If you’re patient enough to implement this strategy for 6 months.
5. Isolate Flat Muscles
The fifth and final training strategy for fuller muscles is not via expansion of fascia, but rather by placing training stress precisely where it belongs.
The whole point of training is to stress the body, then let it adapt. In terms of bringing up a weak or flat muscle, we must ensure that the stress of training is placed right on that muscle. That’s the only way to ensure it’s the one that will adapt.
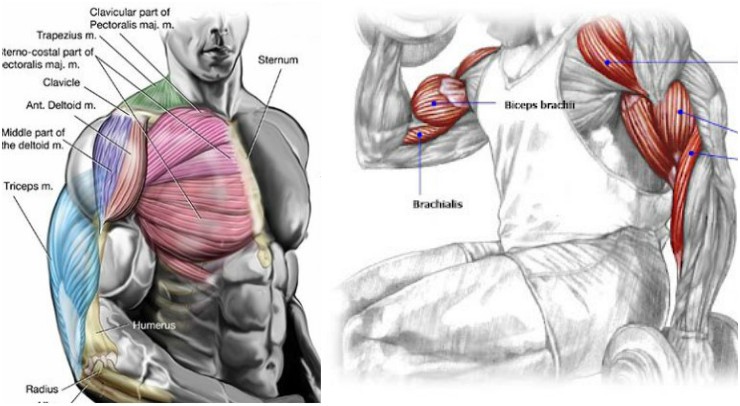
For example, let’s say you’re doing barbell bench press to fill out your pecs. If, your triceps end up doing the majority of the work, then it’s your triceps that will get bigger and stronger.
Staying with this example, there are a couple of ways to ensure that the pecs do the work and receive the stimulation, as opposed to the triceps. One way is to isolate the pecs with another exercise immediately prior to doing the compound, multi-joint bench press.
For example, do dumbbell flyes first, then immediately go into the barbell press. The lighter weight you will use on the bench press is the more beneficial. But you can rest assure that it’s your pre-exhausted pecs that are the weak link during the barbell press. Meaning your pecs, as opposed to your triceps, will be the muscle that’s forced to adapt via hypertrophy.
In addition to pre-exhaustion or pre-isolation, simply doing isolation exercises themselves is perfect for filling out a weak muscle.
It’s better to use compound movements like squats, deadlifts and the bench press. But when it comes to improving a specific body part, isolation exercises like leg extensions, straight arm pull downs, and flyes are often just what you need.
Isolation exercises aren’t optimal for improving overall strength, but they help fill out a lagging body part by placing all of the stress of that exercise on that particular body part.
If you have a hard time feeling a particular muscle work during a compound movement that really should hit that muscle well, try doing the isolation exercise first, before moving on to the compound exercise.
Not only does this provide a bit of pre-exhaustion similar to when they’re done in a superset fashion, but it also works by neurologically warming up this otherwise hard to target muscle.
As an example, let’s say you have a hard time feeling your upper back (i.e., mid traps, rhomboids) work while doing overhand barbell rows. Try doing reverse flyes as your first exercise. Then move on to rows. You’ll find that you’ll feel your upper back much better on the rows than if you did them first.